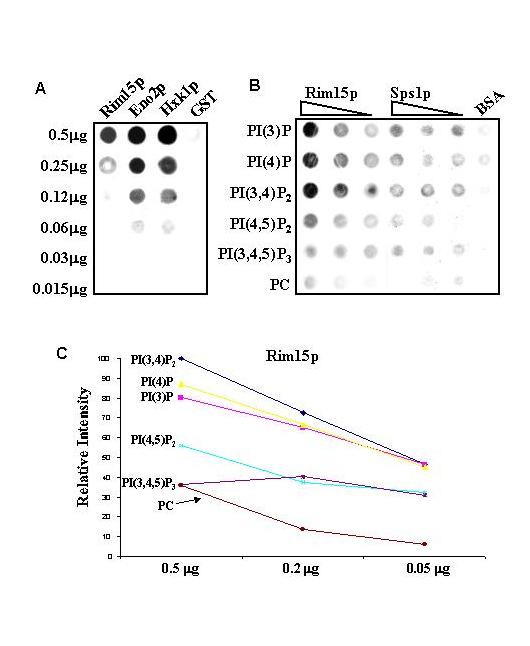
Using two types of conventional methods to confirm protein-lipid interactions detected by the proteome microarrays (49). A. PI(4,5)P2 liposomes were first adhered to a nitrocellulose membrane, which was blocked by BSA; a dilution series of Rim15p, Eno2p, and Hxk1p, and a GST control were used to probe the membrane. The bound proteins were detected using the anti-GST antibodies and an ECL kit. B. A reverse assay was carried out to test potential protein-lipid interactions. The proteins were prepared and spotted onto nitrocellulose filters in a dilution series and probed with the six differentliposomes. As a control, the six liposomes were also added to BSA blocked membrane. After extensive washing, the bound liposomes were detected using an HRP-conjugated streptavidin and an ECL kit. C. Linear correlation between the binding signals and the amounts of Rim15p in a membrane assay. When its liposome-binding signals from the membrane assay (Fig. 4B) were plotted against the concentration gradient of the spotted Rim15p, a linear correlation between the binding signals and the amounts of Rim15p was revealed. PI(4)P showed the highest affinity to Rim15p, at least three times higher than the control PC. As indicated by the chart, PI(4)P, PI(3,4)P2, PI(3)P, and PI(4,5)P2 binding showed a linear correlation with the Rim15p concentration gradient.