(click picture for expanded view)

(click on picture to enlarge)
confirmed by a second investigator, and
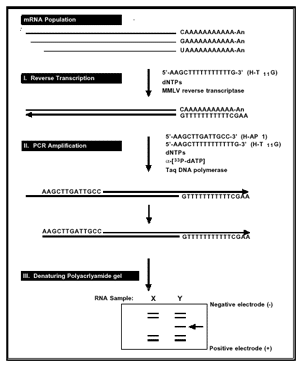
expressed as a single digit numeric. A part of the bands were quantified using
PhosphorImager System (Molecular Dynamics).
image obtained from www.genehunter.com